Schematic Route Sketches
Path Schematization for Route Sketches
One important use of visualizations of routes in road networks is to help orientation while driving. Traditional road maps with their uniform scale are good for giving a general idea of the route, but often do not succeed in showing details of the route within the start and destination region.
Manually generated route sketches do not suffer from this problem. Hence, we consider the problem of automatically generating route sketches. Users generally have a rough conception—the mental map—of the route, hence, the sketch must sufficiently resemble the original route. We achieve this by requiring that in the new drawing the left-right and top-bottom relationship between all important nodes in the original route is maintained. Further, to enhance readability a minimum edge length is introduced and to reduce the visual complexity the admissible edge slopes are restricted.
Experimental Results
[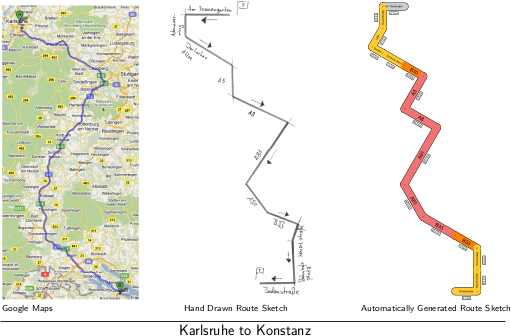 ]
The example route from Karlsruhe, Germany to Konstanz, Germany shows the result of our method.
The traditional road map (picture on the left) and the hand-drawn route sketch differ in that the latter displays road details in Karlsruhe and in Konstanz more clearly. While in the hand-drawn route sketch all parts of the route are clearly visible, the road map provided by google maps only shows the highways in sufficient detail. Although the route is skewed in the hand drawn route sketch the overall shape, i.e., the mental map, is preserved. Our algorithms automatically generate route sketches that mimick the major characteristics of hand drawn route sketches. So, each street is discernable while the rough shape of the original route can be recognized. An experimental evaluation showed that our technique generates good route sketches within a reasonable time frame.
]
The example route from Karlsruhe, Germany to Konstanz, Germany shows the result of our method.
The traditional road map (picture on the left) and the hand-drawn route sketch differ in that the latter displays road details in Karlsruhe and in Konstanz more clearly. While in the hand-drawn route sketch all parts of the route are clearly visible, the road map provided by google maps only shows the highways in sufficient detail. Although the route is skewed in the hand drawn route sketch the overall shape, i.e., the mental map, is preserved. Our algorithms automatically generate route sketches that mimick the major characteristics of hand drawn route sketches. So, each street is discernable while the rough shape of the original route can be recognized. An experimental evaluation showed that our technique generates good route sketches within a reasonable time frame.
Publications
Journal articles
Conference articles
- Andreas Gemsa, Martin Nöllenburg, Thomas Pajor, and Ignaz Rutter.
On d-regular Schematization of Embedded Paths.
In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Computer Science (SOFSEM'11) volume 6543 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 260-271. Springer, January 2011.
[ html ][ pdf ] - Daniel Delling, Andreas Gemsa, Martin Nöllenburg, and Thomas Pajor.
Path Schematization for Route Sketches.
In: Proceedings of the 12th Scandinavian Symposium and Workshop on Algorithm Theory (SWAT'10) volume 6139 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 285-296. Springer, June 2010.
[ html ][ pdf ]
Master's Thesis
- Schematized Visualization of Shortest Paths in Road Networks.
Andreas Gemsa.
Master's thesis, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Fakultät für Informatik, November 2009.
[ pdf ]
